PyQT
This section contains advanced information about scripting in Pixyz Studio.
Since the 2020.1 release, Pixyz Studio integrates the PyQT Python plugin.
Use this plugin to create your own advanced interactions and user interface (UI) in addition to the existing plugin system.
WARNING Most of the features in this section are experimental and highly unstable.
This example shows how you can create a custom widget:
# In the Scripting pane in Studio, select Synchronous Execution and run the following script.
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget
root = QWidget()
root.resize(250, 0)
root.setWindowTitle("Hello world!")
root.show()
Read more about the capabilities of this module in the PyQT documentation.
Synchronous mode vs asynchronous mode
You must run UI function calls on the main thread, that is, in synchronous mode. To force this mode, select Synchronous Execution in the Scripting pane in Studio:

If you run the script within a Studio plugin, add the key value sync="true" to the declaration of the main function in the plugin.xml file:
…
<function name="main" scriptFile="main.py" sync="true">
…
In synchronous mode, all tasks run on the main thread. The synchronous mode prevents the update of the viewer and the rest of the graphical user interface (GUI).
WARNING Studio may freeze when you run costly algorithms in synchronous mode, for example during tessellation or decimation.
Core GUI
Some functions of the CoreGUI module bind PyQT interfaces to Studio. To access the list of functions, press F12 in Studio.
The following table shows some of these functions:
|
Function |
Description |
|
coregui.applyApplicationStyle |
Applies the Studio stylesheet to the widget. |
|
coregui.dockWidget |
Docks the widget to the Studio graphical user interface (GUI) as a standard pane. |
|
coregui.getPropertyWidget |
Gets the specified widget, for example the visibility widget on an occurrence. |
|
coregui.getFunctionWidget |
Gets the specified widget, for example the Tessellation widget. |
Example
This example shows a custom widget:
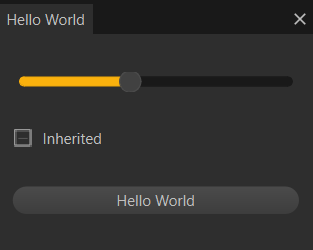
To create this widget, run this script:
# In the Scripting pane in Studio, select Synchronous Execution and run the following script.
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QSlider, QPushButton
main_occurrence = None
def slider_value_changed(value):
"""
This method is called each time the slider value changes
"""
global main_occurrence
core.setProperty(main_occurrence, 'Transform', str(geom.fromTRS(pxz.geom.Point3(0,0,0), pxz.geom.Point3(0,0,0), pxz.geom.Point3(1, 1+value, 1))))
view.fit([main_occurrence])
def button_clicked():
"""
This method is called each time the Invert Orientation button is clicked
"""
global main_occurrence
scene.applyTransformation(main_occurrence, geom.fromTRS(pxz.geom.Point3(0,0,0), pxz.geom.Point3(0,3.14,0), pxz.geom.Point3(1,1,1)))
view.fit([main_occurrence])
def create_text_occurrence(text):
"""
Creates a Text in the viewer and fits the view around it
"""
occurrence = scene.createOccurrenceFromText(text)
scene.setParent(occurrence, scene.getRoot(), False, 0)
view.fit([occurrence])
view.setViewerProperty('DoubleSided', 'True', -1)
return occurrence
def main():
global main_occurrence
# Create a "Hello World" shape in the scene
main_occurrence = create_text_occurrence('Hello World')
# Inititalize PyQT layout and main widget
layout = QVBoxLayout()
main_widget = QWidget()
# Add a Slider widget to the layout -> all this is PyQT
slider_widget = QSlider(QtCore.Qt.Horizontal)
slider_widget.setMinimum(0)
slider_widget.setMaximum(5)
slider_widget.valueChanged.connect(slider_value_changed)
layout.addWidget(slider_widget)
# Get the widget associated to the Text occurrence visibility and add it to the layout
occurrence_visibility_widget = coregui.getPropertyWidget(main_occurrence, 'Visible')
layout.addWidget(occurrence_visibility_widget)
# Create a PyQT Button widget and add it to the layout
push_button_widget = QPushButton('Invert Orientation')
push_button_widget.clicked.connect(button_clicked)
layout.addWidget(push_button_widget)
# Bind the main widget and the layout, dock it Studio interface and apply Studio style
main_widget.setLayout(layout)
coregui.dockWidget(main_widget, 'Hello World')
coregui.applyApplicationStyle(main_widget)
main()