About Instances & Prototypes
What is instantiation?
Generally speaking, instantiation is a concept used to repeat the same part, or subassembly multiple times within a CAD/3D model or 3D scene.
It is used to ease CAD design modification at the engineering stage, when the same subassembly is repeated several times in a complex model (the 4 wheels of a car for example).
At the visualization stage, instantiation is also useful for performance optimization: in a 3D viewer, what is displayed as multiple parts are multiple instances of the same part, thus demanding less computing power.
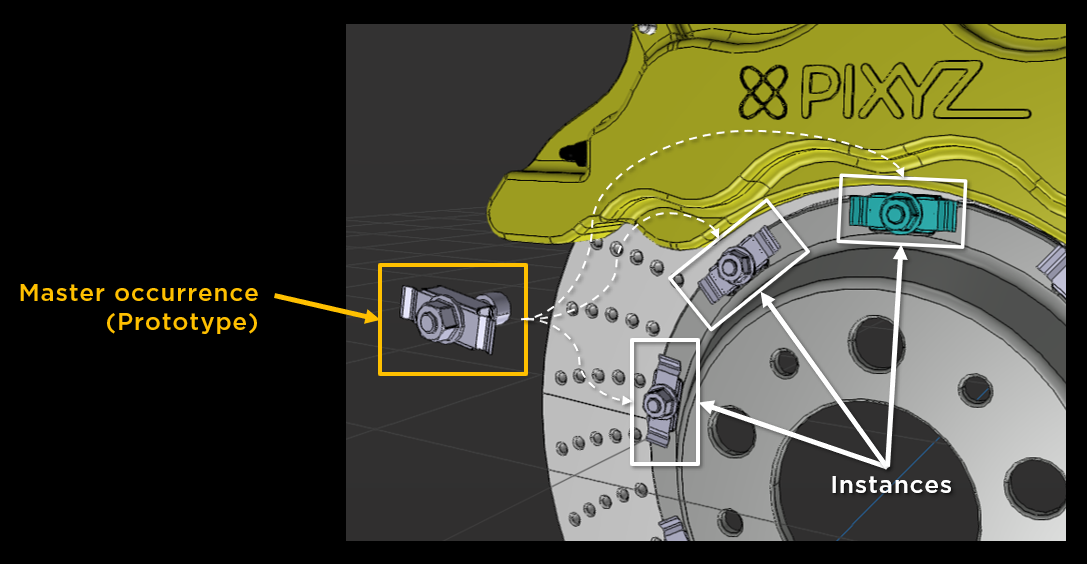
Instantiation in Pixyz
Within a Pixyz scene, instances derive from the same master occurrence, called a prototype.
A prototype is an occurrence of any type (Part occurrence, Assembly occurrence…) that can be referenced by other occurrences, allowing to create instantiation behavior.
So, each instance is an occurrence, with its own properties (transformation matrix, material…) that can override its prototype's own properties.
Very often, CAD/3D models include instances that are retrieved at import in Pixyz Studio, and kept at export (if the export format allows it).
Instantiation can also be created directly within Pixyz Studio, by duplicating subparts of the Product Structure (interactively or through Python scripting), using the Replace By tool, or using the Create Instances By Similarity function.
Practical example
Say you have a table and 4 chairs around, where the chairs are all the same.
The table is made of 50 triangles, and each chair is made of 100 triangles.
If the chairs are not instantiated, each one counts for 100 triangles, so the total of triangles in the scene is 50 + 4 x 100 = 450 triangles
If the chairs are instantiated, then one chair mesh is reused 4 times, for a total of 50 + 100 = 150 triangles.
That is 300 less triangles to load, and to store in file, resulting in reduced file size!
Use instantiation as much as possible as it offers free geometry reduction!