CAD vs Mesh
CAD models that have been created with CAD software aren't tessellated. Examples of CAD software are CATIA, NX, SolidWorks, Alias, and STEP. CAD models contain exact parametric geometries.
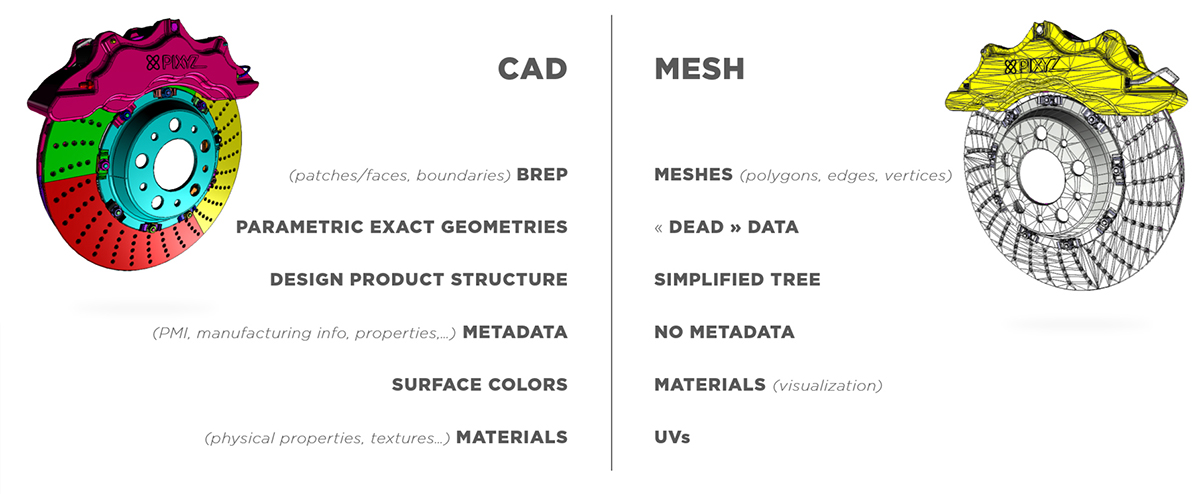
CAD geometries are also referred to as, among others:
- Boundary representation (B-rep or BREP)
- Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS)
- Constructive solid geometry (CSG)
CAD bodies and CAD surfaces are made up of CAD faces, which are delimited by boundaries. CAD faces are also referred to as CAD patches.
To display CAD faces in a 3D application, you must create tessellated meshes, that is, polygonal models, from CAD geometries.
CAD models may contain additional engineering and design information, such as metadata and product manufacturing information (PMI). You can target data preparation based on this information.
Using digital content creation software (DCC), you can natively create tessellated meshes. Examples of DCC software are Maya, 3DS Max, Blender, and Modo. For example, you can export meshes as .fbx files. Then, for further optimization, you can reimport the exported files.
Meshes may contain, among others, these attributes:
- Normals, which you can use to define how meshes react to light
- Textures coordinates, which you can use to display textures on meshes
You can keep this information or recreate it.